A new discipline in the era of SGE and E-E-A-T
[ad_1]
With the rise of large language models (LLMs), mass-produced AI content is becoming more prevalent and the risk of incorrect information spreading also grows.
Thus, it is increasingly important for search engines and answer machines to identify trustworthy and authoritative sources and weed out all others.
This recent evolution in SEO requires new tasks, skills and roles.
This article explores a new potential marketing discipline called “digital authority management” and the role of E-E-A-T in a new search environment like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE).
Quality verification for Google search: E-E-A-T’s influence and role
The huge influence of E-E-A-T in today’s Google search can no longer be ignored.
An author’s general authority and credibility become more significant at a time when mass-produced, identical AI content and disinformation are rampant.
Below is a summary of possible areas of influence of E-E-A-T in Google search:
Rankings in the classic Google search results
At least since the documentation of the Google Core Updates, the importance of E-E-A-T as a ranking influence has been confirmed since 2018.
Display in Google Discover and Google News
According to Google, E-E-A-T is used for playout on Google News and Discover one of the three most important factors.
Helpful content system
E-E-A-T plays an important role here. According to the Helpful Content System documentation:
“Google’s automated systems are designed to use many different factors to rank great content. After identifying relevant content, our systems aim to prioritize those that seem most helpful. To do this, they identify a mix of factors that can help determine which content demonstrates aspects of experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness, or what we call E-E-A-T.”
Showing indicative snippet elements like star reviews, FAQ snippets, sitelinks
Rich snippet elements are not displayed for every result, even though they have implemented the necessary structured data.
From my observation, there must be a sitewide factor that may or may not show these items depending on the topic. E-E-A-T would be a suitable standard for choosing results that are getting rich snippets.
Indexing
One of the big challenges for Google is the cost-effective crawling and indexing of URLs and content. In times of mass content created with AI, this challenge increases exponentially.
Google’s Gary Illyes recently commented on indexing in the Search Off the Record podcast. He pointed out that proportionately less content will be indexed in the future and that website owners should pay more attention to the quality of their content so that it is indexed.
E-E-A-T would be a way to exclude entire website areas from indexing in a scalable way without having to crawl every single URL.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
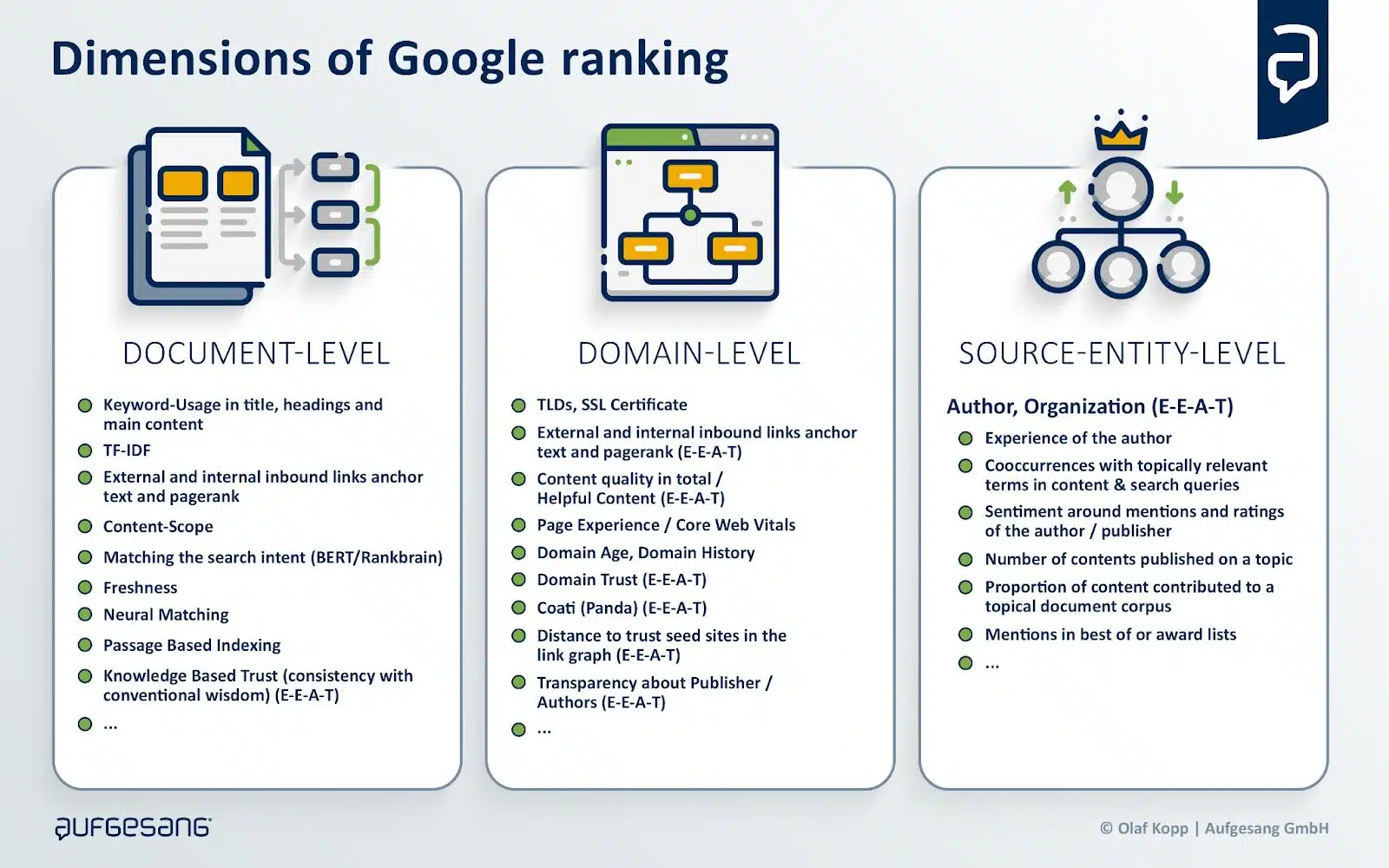
When it comes to E-E-A-T, I often read that one should optimize at the document level, but it is quickly forgotten that, in addition to the main content (MC), it is primarily about the evaluation of the author or the content creator. I call them “source entities.”
The search quality rater guidelines clearly state that the main focus should be on the reputation of the website and the content creator in the page quality rating.

Reputation can be used analogously to trust, which is the focus of E-E-A-T.
Here, we need to distinguish between the source entity (publisher or author) and the website (domain).
Websites are to be understood as digital representations of source entities, so they are closely related to each other.
An E-E-A-T evaluation takes place primarily on a meta level for the website, source entity, or content creator.
The reputation of a website should be checked based on the information published there and, above all, by researching independent sources such as:
- Reviews.
- References.
- Recommendations by independent experts.
- Forum discussions.
- Wikipedia.

Off-page sources provide information about the source entity on About Us pages and comments on the main content.
It is about evaluating a consistent and qualitative overall picture of the source entity or content creator.
In my article “14 ways Google may evaluate E-A-T,” I have identified over 14 measurable signals that may play a role in E-E-A-T.
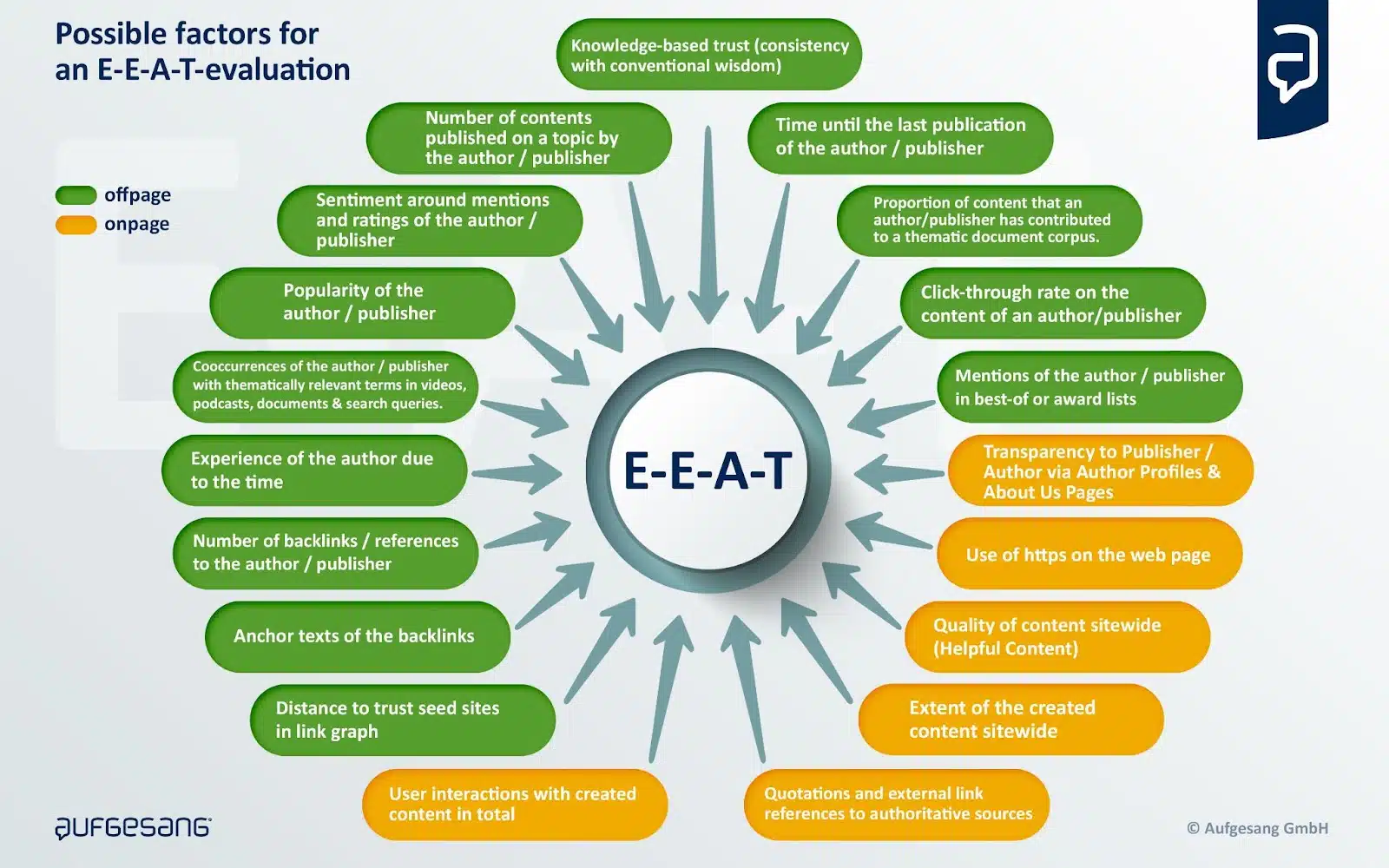
Google has made it clear several times that E-E-A-T is not a direct ranking factor and that there is no uniform E-E-A-T score. Rather, E-E-A-T is a mix of factors that gives an overall picture of experience, expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness in content and the source entity.
E-E-A-T can be understood as a quality classifier that provides content with a ranking bonus after document scoring. This ranking bonus is higher for YMYL topics than other topics and searches.

Possible ranking process including E-E-A-T at Google
Websites can be divided into different quality levels, described in the Google patent, “Website Representation Vector to Generate Search Results and Classify Website.”
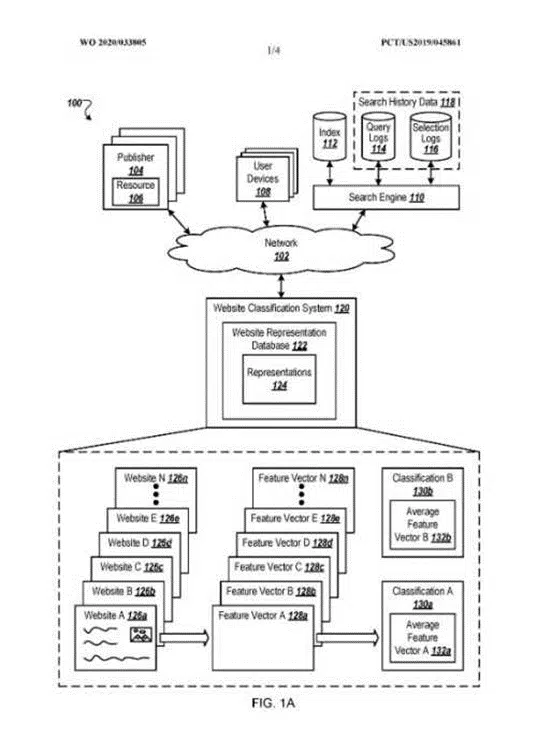
Depending on the level, the ranking bonus can vary.
As we can see, building a reputation, authority and credibility that can be measured by Google plays an increasingly important role in Google rankings.
In How Google may identify and evaluate authors through E-E-A-T, I explain in more detail how Google can evaluate source entities at this meta level.
The possible role of E-E-A-T on generative AI applications like Bard
LLMs such as GPT, BARD or PaLM learn using training data from selected sources. This process takes place as part of natural language understanding.
We have seen LLM-based outputs through ChatGPT and will see more in the future through the AI snapshot box and conversational mode on Google SGE.
For the training data to be as valid as possible, providers of generative AI applications must ensure that the underlying data corpus comes from trustworthy sources.
Google could also use the E-E-A-T concept to select these sources and only access those that belong to a certain quality class.
This would enable Google to update the data corpus for training the LLMs on a big scale. The facts from the Knowledge Graph could be used for fact-checking.

The link boxes in the snapshot box refer to results related to the AI-generated response, according to Google.
Because the links’ positions are highly visible, Google will have to pay attention to particularly trustworthy sources. Here, too, E-E-A-T can play an important role.

The author’s experience and expertise, the delivery in the new perspective feed should play an important role, according to Google, which suggests the reference to the double E in E-E-A-T.

Future product or solution searches could look like this:

Aim for your products and solutions to be included in topically relevant AI-generated responses by leveraging relevant sources selected as training data for LLMs.
This is the only way to create the necessary co-occurrences of product or company plus topic/product group.
This also turns you into an authoritative brand with a solid reputation for the algorithms.
The role of digital authority management
Building a brand and reputation are originally the task of brand management, marketing and PR – basically, beyond classic SEO.
However, those responsible for brands rarely concern themselves with the effects of their efforts on generating algorithmically measurable signals.
In many companies, SEO and brand management are far apart and don’t often talk to each other. So there is a gap that brand managers and SEOs in most companies have yet to close. I believe digital authority management is the answer.
Digital authority management involves SEO and branding and is responsible for building digital brand to improve visibility in search engines and generative AI-controlled output applications.
A digital authority manager plans and promotes efforts to generate algorithmically measurable signals of topic leadership and brand positioning. In addition, this role is responsible for the consistency of the signals and the digital sentiment around the company.
Here are some approaches to the tasks of a digital authority manager:
- Positioning of authors or companies as experts.
- Establishing a digitally recognizable themed tour.
- Ensuring the consistency of author and company descriptions in online media.
- Earning and controlling links from authoritative media.
- Designing marketing and PR campaigns that influence brand searches/
- Identifying resources used (by Google) for training LLMs.
- Controlling sentiment-related signals such as ratings.
- Controlling brand-related online samples.
- Managing influencer relations and influencer marketing.
- Closing exchanges with social media, SEO, link building, content creation, PR, marketing and brand management.
Rethinking your digital branding and organizational structure
The significance of building digital brands is growing in the era of generative AI. Digital brand building involves generating signals that work for people and the algorithms of digital gatekeepers such as search engines.
It is time to rethink your corporate structure, break down silos and work toward a user-centric organization.
User-centric companies do not structure themselves according to channels but to user needs. They are also up to speed with technological developments.
Interface disciplines such as digital authority management become more vital to create bridges between departments and make the silos penetrable.

Opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
[ad_2]
Source link




0 Comments